Difference between revisions of "Component: LED Charlieplex (Outputs: LEDs)"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| − | |||
The Charlieplex scheme simply places two LEDs between each combination of two microcontroller control pins. One LED in forward bias the the other LED in reverse bias. | The Charlieplex scheme simply places two LEDs between each combination of two microcontroller control pins. One LED in forward bias the the other LED in reverse bias. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
If all the LEDs you want to drive have the same characteristics then you can wire up like this to use the same current limiting resistors to drive multiple LEDs. | If all the LEDs you want to drive have the same characteristics then you can wire up like this to use the same current limiting resistors to drive multiple LEDs. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:cp_3.jpg]] |
| Line 50: | Line 49: | ||
[http://led.linear1.org/1led.wiz LED Resistor Calculator Tool] | [http://led.linear1.org/1led.wiz LED Resistor Calculator Tool] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Here is an example of a 4-pin setup. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:cp_4.jpg]] | ||
==Downloadable macro reference== | ==Downloadable macro reference== | ||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 22 January 2018
| Author | Matrix Ltd. |
| Version | 1.4 (Release) |
| Category | Outputs: LEDs |
Contents
 LED Charlieplex component
LED Charlieplex component
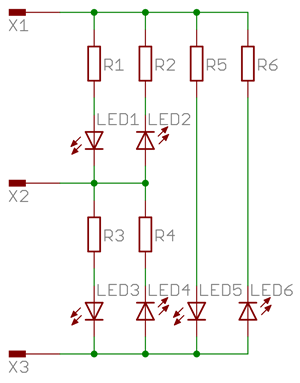
Create an evenly spaced array of LED indicators using a reduced amount of I/O pins. Only one LED can be switched on at once, high speed multiplexing allows multiple LEDs to appear to be lit at once. Each will be connected in line with the standard charlieplex scheme. Set target object to point at any standard LED component to change the style.
Examples
The Charlieplex scheme simply places two LEDs between each combination of two microcontroller control pins. One LED in forward bias the the other LED in reverse bias.
With two control pins you can control up to two LEDs or a single bicolour LED.
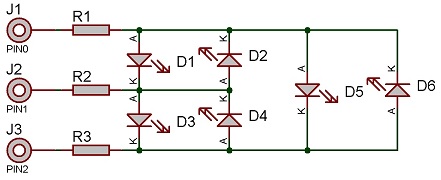
With three control pins you can control up to six LEDs or up to three bicolour LEDs.
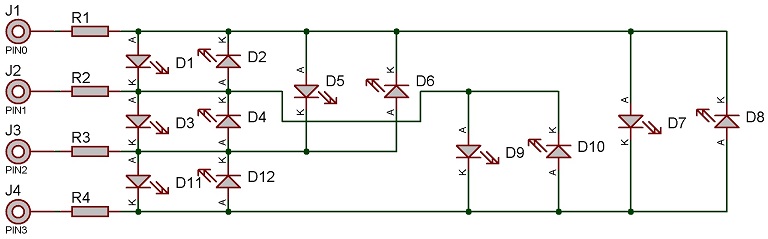
With four control pins you can control up to twelve LEDs or up to six bicolour LEDs.
If all the LEDs you want to drive have the same characteristics then you can wire up like this to use the same current limiting resistors to drive multiple LEDs.
If the LEDs you want to drive have different characteristics then you can wire up like this to use different current limiting resistors for each individual LED.
The value of resistor used can be changed based on the brightness of the LED and power consumption.
This LED Calculator tool is a good resource for calculating the correct LED series protection resistor.
Here is an example of a 4-pin setup.
Downloadable macro reference
LEDOn
Turn on the selected LED
Parameters
- BYTE Index
- Index of the LED to turn on starting from 1.
Return value
- This call does not return a value
AllOff
Turns off all elements
Parameters
- This macro has no parameters
Return value
- This call does not return a value
Simulation macro reference
GetHandle
Retrieves the object handle of the indexed clone.
Returns zero for out of range indexes.
Parameters
- BYTE Index
Return value
Property reference
Pin Count
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name pincount.
The number of pins to dedicate to the charlieplexed output.
LED Count
This property is of type Unsigned integer and can be referenced with the variable name ledcount.
The maximum number of LEDs that can be individually addressed based on the number of pins available.
Pin 0
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name pin0.
Chip pin connection for charlieplexed signal 0
Pin 1
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name pin1.
Chip pin connection for charlieplexed signal 1
Pin 2
This property is of type Single digital pin and can be referenced with the variable name pin2.
Chip pin connection for charlieplexed signal 2
Alignment
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name align.
Which 3D axis to align the copies along.
Spacing
This property is of type Floating point and can be referenced with the variable name spacing.
The distance between LEDs in the array.
LEDs will be spaced symmetrically around the component centre.
Use a negative value to reverse the order of the LEDs.
Width
This property is of type Floating point and can be referenced with the variable name width.
Width of the LED shape.
Height
This property is of type Floating point and can be referenced with the variable name height.
Height of the LED shape.
Depth
This property is of type Floating point and can be referenced with the variable name depth.
Depth of the LED shape.
Reverse
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name reverse.
Reverse the direction of the LEDs.
Show
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name show_label.
Decide what labels to show...
None - no labels are displayed
Name - shows each component's name
Property - shows a particular property of each component (see 'property' below.
Color
This property is of type Color picker and can be referenced with the variable name label_color.
Color of the labels text.
Scale
This property is of type Floating point and can be referenced with the variable name label_scale.
Sets the basic size (text height) of the labels.
Follow Zoom
This property is of type True or false and can be referenced with the variable name label_auto_scale.
Whether labels get bigger and smaller when the panel is zoomed in and out.
Position
This property is of type Fixed list of ints and can be referenced with the variable name label_position.
Set the position of the label relative to the component.