Difference between revisions of "Bot test"
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Author | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Author | ||
| − | | Matrix | + | | Matrix Ltd. |
|- | |- | ||
| width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Version | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Version | ||
| − | | | + | | 2.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Category | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Category | ||
| − | | | + | | Wireless |
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | ==Bluetooth (EB024, Generic AT) component== |
| − | + | Low level routines for controlling a standard AT Bluetooth interface. Also available in the form of the EB024 Bluetooth E-block. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Detailed description== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''No detailed description exists yet for this component'' | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| − | + | ===Making a device discoverable=== | |
| + | |||
| + | Example program to set up the Bluetooth module to be discoverable with a pair key. Any data received is then output onto the LCD component. You can connect to the Bluetooth device using a PC with Bluetooth connection and using software such as Flowcode 6, RealTerm or HyperTerminal. Alternatively you can connect using a smart phone running a terminal emulator app or via another embedded Bluetooth board. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|BluetoothDiscover.fcfx|Bluetooth Discover}} | ||
| + | Script 1 contains the AT commands to setup the Bluetooth device to be discoverable with pair key "1234". | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DiscoverableScript.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Searching for a device=== | ||
| + | Example program to scan for local discoverable Bluetooth devices. For each device found the MAC address is displayed on to the LCD. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|BluetoothInquire.fcfx|Bluetooth Inquiry}} | ||
| + | ===Connecting to a device=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example program to connect to a specific Bluetooth device address and send data to the device. | ||
| + | {{Fcfile|BluetoothConnect.fcfx|Bluetooth Connect}} | ||
| + | The device MAC address is specified using the "CreateCommandString" and "SendCommand" macros. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ConnectToMAC.jpg]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 50: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''StringRead''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | colspan="2" | Returns the ASCII value of character idx of the Response string. |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | idx |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Needs to be a equal to or less than the string length of the response in order to retrieve a valid character. |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| Line 51: | Line 68: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''SendScript''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Sends Script idx Note that the general property Number of Scripts needs to be set so that it allows the scripts to be accessed and sent. Returns 0 for success and 1 for error |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | idx |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Refers to the Script page to send (1-4). |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | ||
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 74: | Line 86: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''SendCommand''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Sends the command buffer. Returns 1 for success in sending the command. Returns 0 for errors. |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | ExpectEcho |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Remote module automatically echos back data: 1 = On (Expect echo), 0 = off |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | SendCR |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Automatically adds \n to the end of the command data: 1 = append CR, 0 = no CR. |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| Line 97: | Line 109: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''CreateCommandString''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Assigns a string of characters to the Command buffer. Returns 1 for success in adding the characters to the buffer. Returns 0 for errors, including Buffer overflow. |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-string-icon.png]] - STRING |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Data |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | ||
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 125: | Line 127: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''StringReceive''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Checks for a response string. Returns the length of the response string if one is present otherwise returns 0. |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | ||
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 153: | Line 140: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''CreateCommand''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Adds a single characters to the end of the Command buffer. Returns 1 for success in adding the characters to the buffer. Returns 0 for errors, including Buffer overflow. |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Character |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | ASCII value or single character, |
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | ||
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 176: | Line 158: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Send_byte''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | ByteVal |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-void-icon.png]] - VOID |
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 194: | Line 176: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''WaitForResponse''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Waits for a response message of type response_code for timeout ms. Returns: 0 for a Response of type response_code 255 (0xFF) for a timeout or invalid response Response string length for any Response not of type response_code |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | response_code |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | 1:OK / 2:ERROR / 3:CONNECT / 4:NO CARRIER / 5:AUDIO / 6:PAIR / 7:RING |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | timeout |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | The timeout value will need to set to allow sufficient time for the response to arrive. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9- | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-u8-icon.png]] - BYTE |
| width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 219: | Line 201: | ||
| width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Initialise''' | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Initialise''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Required to be used whenever the Bluetooth component is used in a program. Initialises the Bluetooth component ready for use. |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 236: | Line 218: | ||
| width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Properties''' | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Properties''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Command Buffer Size | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Maximum number of bytes that can be stored in the outgoing command buffer. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Response Buffer Size | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Maximum number of bytes that can be stored in the incoming response buffer. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Script Count |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Controls how many AT scripts are stored into non-volatile memory | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-11-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Script 1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Data to send for script 0, each command should be terminated with a carriage return |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9- | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Connections''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Channel |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | UART Channel selector Software channels are bit banged using generic I/O pins but are not as reliable as hardware channels. Hardware channels use the selected peripheral on-board the target microcontroller. |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-5-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-5-icon.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | TX |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Pin to be used for Transmit data |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-5-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-5-icon.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | RX |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Pin to be used for Receive data |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Use Flow Control |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Flow Control (Handshake) enable or disable. On: Two I/O pins are used to control the flow of data in and out of the device. Off: Flow control is disabled. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Baud Options |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Baud rate option selector |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-14-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Baud Rate |
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="2" | | | colspan="2" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Simulations''' |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90% | + | | width="90%" | Console Columns |
|- | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of characters that can be displayed on a single line of the console. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-7-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Console Data |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Selects if the console data is automatically generated or not |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-7-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-7-icon.png]] | ||
| width="90%" | Scope Traces | | width="90%" | Scope Traces | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | Selects if the scope traces are automatically | + | | colspan="2" | Selects if the scope traces are automatically added to the data recorder window or not. Simulation - draws an approximation of the UART data onto the scope trace. ICT - sets up the scope trace for incoming data and adds UART packet decoding at the correct BAUD. |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | Data Source |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Simulation data source used to allow the component to connect to various remote devices Nothing - Simulation data is ignored COM port - Routes the communication data to and from a physical or virtual COM port API - Routes the communication data via a data API component on the Panel. |
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | ||
| width="90%" | API | | width="90%" | API | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | colspan="2" | | + | | colspan="2" | Selects whichAPI component to route the communication data via. Add API components to the panel before they will be available in this list. API components are available from the Comms component category. |
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:33, 31 August 2021
| Author | Matrix Ltd. |
| Version | 2.0 |
| Category | Wireless |
Contents
Bluetooth (EB024, Generic AT) component
Low level routines for controlling a standard AT Bluetooth interface. Also available in the form of the EB024 Bluetooth E-block.
Detailed description
No detailed description exists yet for this component
Examples
Making a device discoverable
Example program to set up the Bluetooth module to be discoverable with a pair key. Any data received is then output onto the LCD component. You can connect to the Bluetooth device using a PC with Bluetooth connection and using software such as Flowcode 6, RealTerm or HyperTerminal. Alternatively you can connect using a smart phone running a terminal emulator app or via another embedded Bluetooth board.
![]() Bluetooth Discover
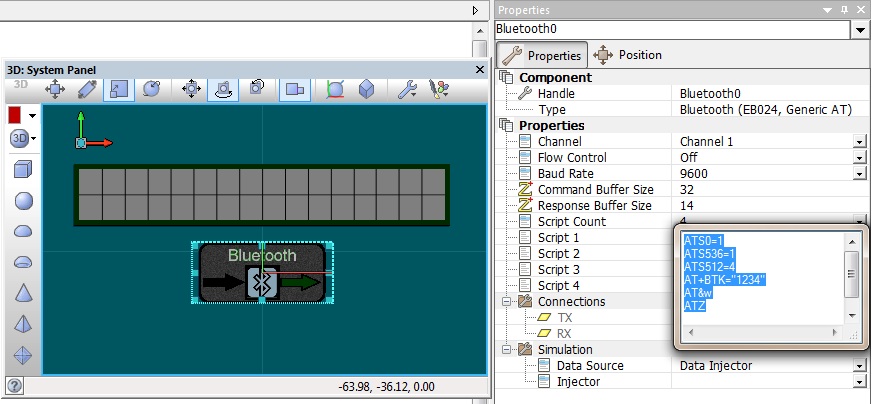
Script 1 contains the AT commands to setup the Bluetooth device to be discoverable with pair key "1234".
Bluetooth Discover
Script 1 contains the AT commands to setup the Bluetooth device to be discoverable with pair key "1234".
Searching for a device
Example program to scan for local discoverable Bluetooth devices. For each device found the MAC address is displayed on to the LCD.
![]() Bluetooth Inquiry
Bluetooth Inquiry
Connecting to a device
Example program to connect to a specific Bluetooth device address and send data to the device.
![]() Bluetooth Connect
The device MAC address is specified using the "CreateCommandString" and "SendCommand" macros.
Bluetooth Connect
The device MAC address is specified using the "CreateCommandString" and "SendCommand" macros.
Downloadable macro reference
| StringReceive | |
| Checks for a response string. Returns the length of the response string if one is present otherwise returns 0. | |
| Return | |
| Send_byte | |
| ByteVal | |
| Return | |
| Initialise | |
| Required to be used whenever the Bluetooth component is used in a program. Initialises the Bluetooth component ready for use. | |
| Return | |