Difference between revisions of "Component: Device Helper (Matrix Tools)"
From Flowcode Help
Jump to navigationJump to search (XML import) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {| style="width:50%" | |
| − | |||
| − | {| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="20%" style="color: gray;" | Author | + | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Author |
| Matrix TSL | | Matrix TSL | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="20%" style="color: gray;" | Version | + | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Version |
| − | | 1.1 | + | | 1.1 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="20%" style="color: gray;" | Category | + | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Category |
| Matrix Tools | | Matrix Tools | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==Device Helper component== | ||
| + | A purely cosmetic component for viewing the details specific to your current selected target microcontroller. Lists stats like ADC resolution, ADC channels, UARTs, SPI, PWM, RAM, ROM etc | ||
| − | == | + | ==Component Source Code== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Please click here to download the component source project: [https://www.flowcode.co.uk/wiki/componentsource/FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx] | |
| − | |||
| + | Please click here to view the component source code (Beta): [https://www.flowcode.co.uk/FlowchartView/?wfile=componentsource/FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Detailed description== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''No detailed description exists yet for this component'' | |
| − | + | ==Examples== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
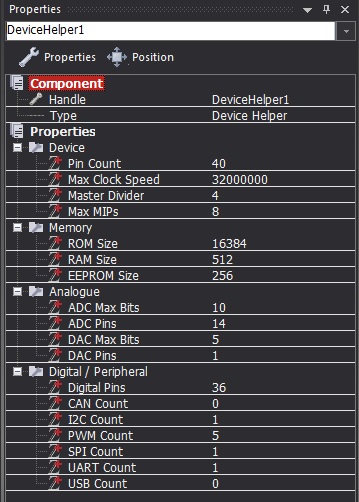
| − | + | By simply adding the device helper component to your project and selecting it on the panel you can see all the following statistics regarding your current selected microcontroller in the properties window. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Dev_Helper.jpg]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Macro reference== | |
| − | + | ==Property reference== | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" | [[File:Fc9-prop-icon.png]] | |
| − | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Properties''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | |
| − | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Device | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] |
| − | + | | width="90%" | Pin Count | |
| − | Used for high speed on board communications e.g. Sensors, Memory | + | |- |
| − | + | | colspan="2" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | |
| − | + | | width="90%" | Max Clock Speed | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) | + | | colspan="2" | Maximum frequency the device can operate. |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | Used for on board and off board communications e.g. RS232, Bluetooth, GPS, GSM | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] |
| − | + | | width="90%" | Master Divider | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | colspan="2" | Number of clock cycles per single device instruction. | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | |
| − | Universal Serial Bus (USB) | + | | width="90%" | Max MIPs |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | Used for interconnective communications with high end equipment such as PCs. | + | | colspan="2" | Million Instructions Per Second (MIPS) Number of complete instruction cycles per second based on the max clock speed and instructions per clock divided by 1 million. Note that some instructions such as decisions can take multiple instructions to complete. |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Memory | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | ROM Size | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of bytes available for ROM storage. ROM - Read Only Memory - Contains the Flowcode program as well as other constants such as strings | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | RAM Size | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of bytes available for RAM storage. RAM - Random Access Memory - Contains the Flowcode variables as well as the operational stack | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | EEPROM Size | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of bytes available for EEPROM storage. EEPROM - Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory - Contains user data that can persist when the power is removed | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Analogue | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | ADC Max Bits | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Maximum number of bits used for an ADC conversion which dictates the maximum reading the ADC can generate. 8 bits = 0 - 255 10 bits = 0 - 1023 12 bits = 0 - 4095 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | ADC Pins | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of pins capable of reading an analogue input. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | DAC Max Bits | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Maximum number of bits used for an DAC conversion which dictates the output resolution of the DAC. 5 bits = 0 - 31 8 bits = 0 - 255 10 bits = 0 - 1023 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | DAC Pins | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of pins capable of outputting an analogue voltage. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Digital / Peripheral | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Digital Pins | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Number of pins capable of reading a digital input and/or writing a digital output. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | CAN Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Controller Area Network (CAN) Used for fixed system architecture in noisy environments e.g. Cars and Automotive | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | I2C Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Used for on board communications e.g. Sensors, Memory | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-10-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | I2C Modes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | H-Bridge Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | PWM Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Pulse Width Modulation Output (PWM) Useful for analogue style outputs. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | SPI Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Used for high speed on board communications e.g. Sensors, Memory | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | UART Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) Used for on board and off board communications e.g. RS232, Bluetooth, GPS, GSM | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-21-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | USB Count | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Universal Serial Bus (USB) Used for interconnective communications with high end equipment such as PCs. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:09, 7 February 2023
| Author | Matrix TSL |
| Version | 1.1 |
| Category | Matrix Tools |
Contents
Device Helper component
A purely cosmetic component for viewing the details specific to your current selected target microcontroller. Lists stats like ADC resolution, ADC channels, UARTs, SPI, PWM, RAM, ROM etc
Component Source Code
Please click here to download the component source project: FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx
Please click here to view the component source code (Beta): FC_Comp_Source_Device_Helper.fcfx
Detailed description
No detailed description exists yet for this component
Examples
By simply adding the device helper component to your project and selecting it on the panel you can see all the following statistics regarding your current selected microcontroller in the properties window.