Difference between revisions of "Component: PWM (Internal) (General Output)"
| (14 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Version | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Version | ||
| − | | | + | | 1.0 |
|- | |- | ||
| width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Category | | width="20%" style="color:gray;" | Category | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==PWM (Internal) component== | ==PWM (Internal) component== | ||
Pulse Width Modulation, a versitile way of generating a digital pulse using mark / space modulation. Uses the capture compare peripherals onboard most Microcontrollers to generate accurate waveforms without any intervention from the processor. Useful for generating audio, controlling the speed of motors, brightness of LED etc. | Pulse Width Modulation, a versitile way of generating a digital pulse using mark / space modulation. Uses the capture compare peripherals onboard most Microcontrollers to generate accurate waveforms without any intervention from the processor. Useful for generating audio, controlling the speed of motors, brightness of LED etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Component Source Code== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Please click here to download the component source project: [https://www.flowcode.co.uk/wiki/componentsource/FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Please click here to view the component source code (Beta): [https://www.flowcode.co.uk/FlowchartView/?wfile=componentsource/FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx] | ||
==Detailed description== | ==Detailed description== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 30: | Line 52: | ||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 48: | Line 86: | ||
Digital PWM trace | Digital PWM trace | ||
| − | [[File:PWMDigital. | + | [[File:PWMDigital.png]] |
| Line 55: | Line 93: | ||
{{Fcfile|PWM_fader.fcfx|PWM Fader}} | {{Fcfile|PWM_fader.fcfx|PWM Fader}} | ||
| − | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Macro reference== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===ChangePeriod=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 80: | Line 121: | ||
| + | ===Disable=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 93: | Line 135: | ||
| + | ===Enable=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Enable''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Enables a PWM channel as an output overriding the default output pin state. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-void-icon.png]] - VOID | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===SetDutyCycle=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 111: | Line 168: | ||
| + | ===SetDutyCycle10Bit=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''SetDutyCycle10Bit''' |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | PIC/AVR - Sets the full scale PWM duty cycle based on the current period setting. If period = 255 then Duty of 512 is equal to 50%. 16-bit PICs have a 16-bit period range available. If period = 65535 then Duty of 32768 is equal to 50%. | ||
| + | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-u16-icon.png]] - UINT |
| + | | width="90%" | Duty | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | PWM duty PIC/AVR: 0-1023 16-bit PIC: 0-65535 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-void-icon.png]] - VOID | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-void-icon.png]] - VOID | ||
| Line 124: | Line 187: | ||
| + | ===SetFrequency=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 141: | Line 205: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Property reference== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" | [[File:Fc9-prop-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | ''' | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''Properties''' |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Connections | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Channel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Selects which PWM channel the component is connected to. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-7-icon.png]] |
| + | | width="90%" | Alternative pin | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Allows an alternate pin to be used if available. Note that on some devices you will also have to change this setting in the device configuration. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9- | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-5-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" | | + | | width="90%" | PWM Pin |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Specifies the pin assigned to the PWM channel selected | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-16-icon.png]] |
| + | | width="90%" | Remap Pin | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | colspan="2" | Allows the PWM hardware pin to be reassigned to another pin |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:# | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:# | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | PWM Frequency |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 199: | Line 271: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="2" | Displays the frequency of PWM cycles per second. | | colspan="2" | Displays the frequency of PWM cycles per second. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Calculations | ||
| + | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-15-icon.png]] | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-type-15-icon.png]] | ||
| Line 225: | Line 301: | ||
| colspan="2" | Applies the calculated period and prescaler settings to the PWM component default settings. | | colspan="2" | Applies the calculated period and prescaler settings to the PWM component default settings. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:# | + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#EAE1EA;" | [[File:Fc9-conn-icon.png]] |
| − | | width="90%" style="background-color:# | + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#EAE1EA; color:#4B008D;" | Simulation |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
Latest revision as of 10:26, 20 October 2023
| Author | Matrix Ltd |
| Version | 1.0 |
| Category | General Output |
Contents
PWM (Internal) component
Pulse Width Modulation, a versitile way of generating a digital pulse using mark / space modulation. Uses the capture compare peripherals onboard most Microcontrollers to generate accurate waveforms without any intervention from the processor. Useful for generating audio, controlling the speed of motors, brightness of LED etc.
Component Source Code
Please click here to download the component source project: FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx
Please click here to view the component source code (Beta): FC_Comp_Source_PWM_Output.fcfx
Detailed description
No detailed description exists yet for this component
Examples
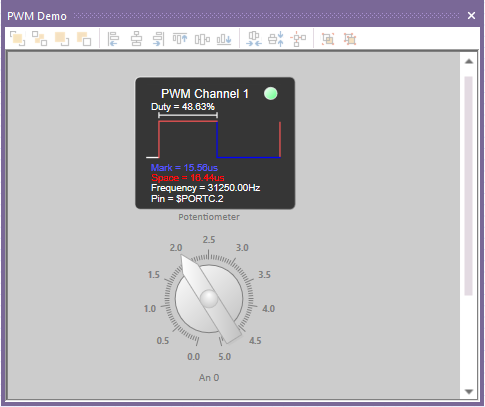
Here is a basic example to control the PWM duty based on an ADC reading.
Digital PWM trace
Here is another basic example which ramps the PWM duty cycle up and down. If the PWM output pin is connected to a LED and series resistor then the LED will smoothly transition between on bright and off.
Macro reference
ChangePeriod
Disable
| Disable | |
| Disables a PWM channel and allows the default output / input state to be resumed | |
| Return | |
Enable
| Enable | |
| Enables a PWM channel as an output overriding the default output pin state. | |
| Return | |
SetDutyCycle
SetDutyCycle10Bit
SetFrequency
| SetFrequency | |
| Sets a PWM of the specifed frequency at a duty of 50% Ideal use is a frequency generator | |
| Frequency | |
| Enter frequency in Hz | |
| Return | |