Difference between revisions of "Component: LCD I2C (Backpack) (Alphanumeric)"
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
[http://www.matrixtsl.com/blog/simplified-communications-i%c2%b2c-and-spi/ Matrix Flowcode Blog: Simplified communications I2C and SPI] | [http://www.matrixtsl.com/blog/simplified-communications-i%c2%b2c-and-spi/ Matrix Flowcode Blog: Simplified communications I2C and SPI] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 94: | Line 96: | ||
==Macro reference== | ==Macro reference== | ||
| + | ===Clear=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 107: | Line 110: | ||
| + | ===PrintString=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 125: | Line 129: | ||
| + | ===PrintAscii=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 143: | Line 148: | ||
| + | ===PrintNumber=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 161: | Line 167: | ||
| + | ===RAMWrite=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 219: | Line 226: | ||
| + | ===BacklightControl=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 237: | Line 245: | ||
| + | ===ClearLine=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 255: | Line 264: | ||
| + | ===Cursor=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 278: | Line 288: | ||
| + | ===Command=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 296: | Line 307: | ||
| + | ===PrintFormattedNumber=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 319: | Line 331: | ||
| + | ===ScrollDisplay=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 342: | Line 355: | ||
| + | ===PrintFloat=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 365: | Line 379: | ||
| + | ===Start=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 378: | Line 393: | ||
| + | ===SetI2CAddress=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 3 February 2023
| Author | Matrix Ltd |
| Version | 2.2 |
| Category | Alphanumeric |
Contents
LCD I2C (Backpack) component
Standard alphanumeric LCD based on a standard I2C control bus. Usually using either a PIC device or Microchip IO expander IC.
Component Source Code
Please click here to download the component source project: FC_Comp_Source_LCD_I2C.fcfx
Please click here to view the component source code (Beta): FC_Comp_Source_LCD_I2C.fcfx
Detailed description
No detailed description exists yet for this component
Examples
A simple example that shows how to use some common functions.
If the display is not showing the expected characters, the I2c address or contrast could be wrong.
It's best to keep the jumper connected since the backlight is enabled by default.
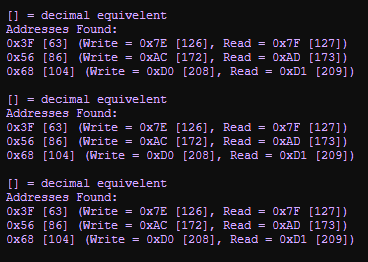
Using an Arduino Uno the correct I2C address can be determined by using an ![]() IC2 Address Sniffer
IC2 Address Sniffer
The I2C address to use is the one within the first set of square brackets.
For example, with my backpack display, the correct address to use is 0x3F [63]:
The other two Addresses i.e. 0x56 [86] and 0x68 [104] is for my 24C32 EEPROM and DS3231 RTC respectively.
Note The I2c addresses scan will repeat every 5seconds.
The sniffer will send data to your PC via UART to USB.
The Arduino range and clones will have it built-in.
More details on I2C can be found here,
Matrix Flowcode Blog: Simplified communications I2C and SPI
Macro reference
Clear
| Clear | |
| Return | |
PrintString
| PrintString | |
| Text | |
| Return | |
PrintAscii
| PrintAscii | |
| Takes the ascii value for a character and prints the character | |
| character | |
| Return | |
PrintNumber
| PrintNumber | |
| Allows you to print a number. This is limited to a signed-INT, -32768 to 32767 | |
| Number | |
| Return | |
RAMWrite
BacklightControl
| BacklightControl | |
| State | |
| Return | |
ClearLine
| ClearLine | |
| Line | |
| Return | |
Cursor
| Cursor | |
| Moves the cursor on the LCD Display | |
| x | |
| y | |
| Return | |
Command
PrintFormattedNumber
ScrollDisplay
| ScrollDisplay | |
| Scrolls the display left or right by a number of given positions. | |
| position | |
| direction | |
| Return | |
PrintFloat
Start
| Start | |
| Startup routine required by the hardware device. | |
| Return | |
SetI2CAddress