Difference between revisions of "Component: Switch (Controls)"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
[[File:switchschematic.jpg]] | [[File:switchschematic.jpg]] | ||
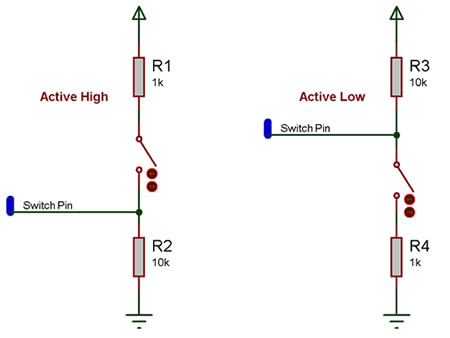
| − | The | + | The polarity setting within the switch properties determines how the relevant bit of the input variable responds when a switch changes state. |
| − | + | This applies only when using switch functions and not when using input command icons. | |
| − | + | * Active High Polarity: When the switch is closed, the voltage on the pin transitions from 0V to the positive supply voltage (either 3.3V or 5V, depending on the microcontroller). As a result, the corresponding bit in the input variable changes from 0 to 1. A pull-down resistor is required for the input pin to ensure it stays at 0V when the switch is open. | |
| − | + | * Active Low Polarity: When the switch is closed, the voltage on the pin transitions from the positive supply voltage to 0V, and again, the relevant bit of the input variable changes from 0 to 1. A pull-up resistor is required for the input pin to ensure it stays at the positive supply voltage when the switch is open. | |
There are some differences depending on the type of switch you have, the above states assume a generic push to make type switch, however a push to break type switch would have reversed logic and a toggle switch can work well with either setup. | There are some differences depending on the type of switch you have, the above states assume a generic push to make type switch, however a push to break type switch would have reversed logic and a toggle switch can work well with either setup. | ||
Revision as of 08:27, 2 May 2025
| Author | Steve Tandy |
| Version | 1.0 |
| Category | Controls |
Contents
Switch component
A 2d switch component.
Component Pack
FREE
Detailed description
No detailed description exists yet for this component
Examples
Here is an example Flowcode program to read the value of a switch.
![]() Switch
Switch
Here is a schematic of how to connect a basic switch to a microcontroller pin.
The polarity setting within the switch properties determines how the relevant bit of the input variable responds when a switch changes state. This applies only when using switch functions and not when using input command icons.
- Active High Polarity: When the switch is closed, the voltage on the pin transitions from 0V to the positive supply voltage (either 3.3V or 5V, depending on the microcontroller). As a result, the corresponding bit in the input variable changes from 0 to 1. A pull-down resistor is required for the input pin to ensure it stays at 0V when the switch is open.
- Active Low Polarity: When the switch is closed, the voltage on the pin transitions from the positive supply voltage to 0V, and again, the relevant bit of the input variable changes from 0 to 1. A pull-up resistor is required for the input pin to ensure it stays at the positive supply voltage when the switch is open.
There are some differences depending on the type of switch you have, the above states assume a generic push to make type switch, however a push to break type switch would have reversed logic and a toggle switch can work well with either setup.
The resistors are required for correct operation because when a microcontroller's input pin is essentially connected to nothing it will pick up noise in the environment and provide inconsistent readings. This state is referred to as floating i.e. the pin is floating. To test this remove the resistors (if possible) and touch the unconnected pin with your finger the output LED from the example file above will toggle on and off at high speed.
Any values of resistor can be used but it is important to keep the smaller resistor at least 10X smaller then the larger resistor to ensure that the pressed state provides at least 0.91% of the required pressed state voltage. For example a active high switch circuit using 1K and 10K resistors should pull up to about 4.54V when the switch is pressed.
(5V / 11K) * 10K = 4.54545V
Downloadable macro reference
| GetState | |
| Reads the state of the switch (true = on, false = off) | |
| Return | |
| SetState | |
| Sets the switch to be on or off. | |
| bState | |
| The new state of the switch (true=on, false=off) | |
| Return | |
Property reference
| Properties | |
| State | |
| Style | |
| Type | |
| On Label | |
| Off Label | |
| Background Colour | |
| Connections | |
| Simulations | |