Difference between revisions of "API Panel.Position.MoveBy"
(XML import) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | |
| − | Moves the object by the given offset relative to its parent | + | |- |
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''MoveBy''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Moves the object by the given offset relative to its parent | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-h32-icon.png]] - HANDLE | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Handle | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | The position or component to update | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-f32-icon.png]] - FLOAT | ||
| + | | width="90%" | X | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Local coordinate X to increment by | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-f32-icon.png]] - FLOAT | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Y | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Local coordinate Y to increment by | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-f32-icon.png]] - FLOAT | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Z | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Local coordinate Z to increment by | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-void-icon.png]] - NONE | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Detailed description== |
| − | + | This moves the position in its own axis by ''X'', ''Y'' and ''Z'' units. That is, the center of the ''Handle'' object is considered to be (0, 0, 0). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | It is a simpler version of [[API Panel.Position.MoveAlong|MoveAlong]] and a compliment to [[API Panel.Position.MoveTo|MoveTo]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
===Calling in a calculation=== | ===Calling in a calculation=== | ||
* Add to a calculation icon: <pre class="brush:[cpp]">::Panel.Position.MoveBy(handle, x, y, z)</pre> | * Add to a calculation icon: <pre class="brush:[cpp]">::Panel.Position.MoveBy(handle, x, y, z)</pre> | ||
| + | |||
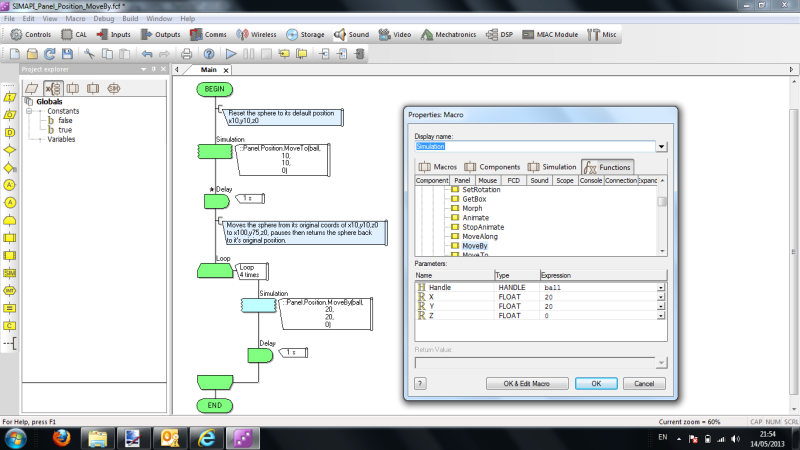
| + | ===Flowcode example file=== | ||
| + | Download {{Fcfile|SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy.fcfx|SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy}} and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example, there are three cubiods that represent Axis X,Y,Z. Note they are coloured exactly as the panel axis indicator which represents your viewing position. There is a sphere also on the panel. | ||
| + | |||
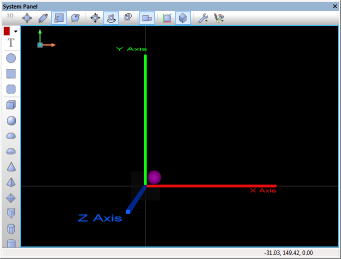
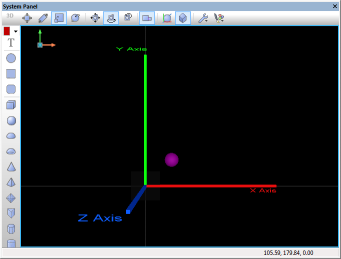
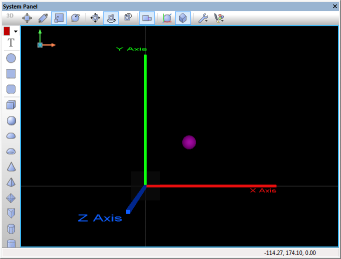
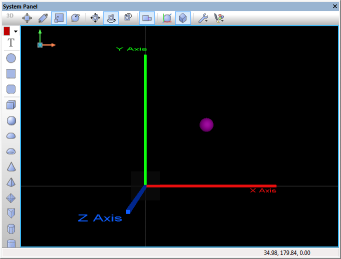
| + | The MoveBy(h,x,y,z) function moves an object from it's original coordinates by a set value represented as an offset from it's original coordinate. In this example, the sphere's original coordinates are x10,y10,z0. The program loops 4 times, each time it calls the MoveBy function increasing the x & y coordinates by 20. This moves the sphere diagonally. As each loop passes the new coordinates would be as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Original Position = (x10,y10,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x30,y30,z0) | ||
| + | # Original Position = (x30,y30,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x50,y50,z0) | ||
| + | # Original Position = (x50,y50,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x70,y70,z0) | ||
| + | # Original Position = (x70,y70,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x90,y90,z0) | ||
| + | |||
| + | After each loop the program pauses a second to allow you to see the effect of the function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The screenshots below show the effect and also highlight the code used by the example. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy_Pic1.png]][[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy_Pic2.png]][[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy_Pic3.png]][[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy_Pic4.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy_Pic0.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Moving a panel item=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Simple example showing how to detect for collisions between objects on the panel. An object moves back and forth between two fixed objects. Each time the moving object hits a static object it will change it's direction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|Collide.fcfx|Collide}} | ||
Latest revision as of 11:41, 16 January 2023
Contents
Detailed description
This moves the position in its own axis by X, Y and Z units. That is, the center of the Handle object is considered to be (0, 0, 0).
It is a simpler version of MoveAlong and a compliment to MoveTo.
Examples
Calling in a calculation
- Add to a calculation icon:
::Panel.Position.MoveBy(handle, x, y, z)
Flowcode example file
Download ![]() SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example, there are three cubiods that represent Axis X,Y,Z. Note they are coloured exactly as the panel axis indicator which represents your viewing position. There is a sphere also on the panel.
SIMAPI_Panel_Position_MoveBy and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example, there are three cubiods that represent Axis X,Y,Z. Note they are coloured exactly as the panel axis indicator which represents your viewing position. There is a sphere also on the panel.
The MoveBy(h,x,y,z) function moves an object from it's original coordinates by a set value represented as an offset from it's original coordinate. In this example, the sphere's original coordinates are x10,y10,z0. The program loops 4 times, each time it calls the MoveBy function increasing the x & y coordinates by 20. This moves the sphere diagonally. As each loop passes the new coordinates would be as follows:
- Original Position = (x10,y10,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x30,y30,z0)
- Original Position = (x30,y30,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x50,y50,z0)
- Original Position = (x50,y50,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x70,y70,z0)
- Original Position = (x70,y70,z0), MoveBy(x20,y20,z0), New position = (x90,y90,z0)
After each loop the program pauses a second to allow you to see the effect of the function.
The screenshots below show the effect and also highlight the code used by the example.
Moving a panel item
Simple example showing how to detect for collisions between objects on the panel. An object moves back and forth between two fixed objects. Each time the moving object hits a static object it will change it's direction.