Difference between revisions of "API Panel.Position.GetEuler"
From Flowcode Help
Jump to navigationJump to search (XML import of API auto-gen) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width:60%; background-color:#FFFFFF;" | |
| − | == | + | |- |
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="background-color:#D8C9D8;" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-comp-macro.png]] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="background-color:#D8C9D8; color:#4B008D;" | '''GetEuler''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | Returns the positions euler angles in (P,Y,R) array | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-h32-icon.png]] - HANDLE | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Handle | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | The position or component to read | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" | [[File:Fc9-h32-icon.png]] - HANDLE | ||
| + | | width="90%" | Target | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | The position or component to convert relative to | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | width="10%" align="center" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | [[File:Fc9-f32-icon.png]] - FLOAT[] | ||
| + | | width="90%" style="border-top: 2px solid #000;" | ''Return'' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ==Detailed description== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Examples== | |
| + | ===Calling in a calculation=== | ||
| + | * Declare a variable 'result' of type FLOAT[] | ||
| + | * Add to a calculation icon: <pre class="brush:[cpp]">result = ::Panel.Position.GetEuler(handle, target)</pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Flowcode example file=== | ||
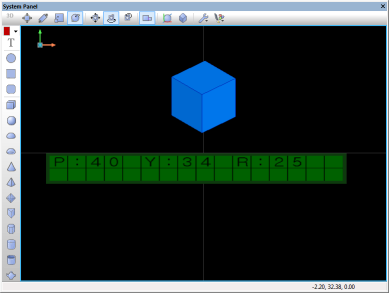
| + | Download {{Fcfile|SIMAPI_Panel_Position_GetEuler.fcfx|SIMAPI_Panel_Position_GetEuler}} and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example a blue cuboid and a LCD are shown on the system panel. When the program starts, the Euler angles of the cuboid are returned into an existing Float Array variable. The Euler angles are then displayed on the LCD display. Be aware in this example the LCD display is showing integer values. The floats are cast to ints. Euler angles are effectively showing the rotational dimensions of the object. | ||
| + | The screenshots below show the effect and also highlight the code used by the example. | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:SIMAPI_Panel_Position_GetEuler_Pic0.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 11:54, 16 January 2023
| GetEuler | |
| Returns the positions euler angles in (P,Y,R) array | |
| Handle | |
| The position or component to read | |
| Target | |
| The position or component to convert relative to | |
| Return | |
Detailed description
Examples
Calling in a calculation
- Declare a variable 'result' of type FLOAT[]
- Add to a calculation icon:
result = ::Panel.Position.GetEuler(handle, target)
Flowcode example file
Download ![]() SIMAPI_Panel_Position_GetEuler and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example a blue cuboid and a LCD are shown on the system panel. When the program starts, the Euler angles of the cuboid are returned into an existing Float Array variable. The Euler angles are then displayed on the LCD display. Be aware in this example the LCD display is showing integer values. The floats are cast to ints. Euler angles are effectively showing the rotational dimensions of the object.
The screenshots below show the effect and also highlight the code used by the example.
SIMAPI_Panel_Position_GetEuler and open it in Flowcode v6. In this example a blue cuboid and a LCD are shown on the system panel. When the program starts, the Euler angles of the cuboid are returned into an existing Float Array variable. The Euler angles are then displayed on the LCD display. Be aware in this example the LCD display is showing integer values. The floats are cast to ints. Euler angles are effectively showing the rotational dimensions of the object.
The screenshots below show the effect and also highlight the code used by the example.