Difference between revisions of "String Manipulation Functions"
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 164: | Line 164: | ||
| − | + | {{Fcfile|Length$.fcfx|Length$ String Example}} | |
| Line 171: | Line 171: | ||
Retrieves a single byte from the specified position in the string. | Retrieves a single byte from the specified position in the string. | ||
| − | Str1= " | + | Str1= "Hello" |
RetVal = Char$(Str1, 0) | RetVal = Char$(Str1, 0) | ||
| Line 195: | Line 195: | ||
Retval is now 'o'. | Retval is now 'o'. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|Char$.fcfx|Char$ String Example}} | ||
| Line 337: | Line 339: | ||
==StringToFloat$(string)== | ==StringToFloat$(string)== | ||
| − | + | Returns a string of numeric ASCII data into a floating point variable. | |
| Line 344: | Line 346: | ||
returns numeric data from the string in floating point form. | returns numeric data from the string in floating point form. | ||
| + | float = StringToFloat$( string ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==ExplodeToIntArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converts a string of numeric ASCII data that has been separated by a designator into an integer Array. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example if TestString = "Hello, 12456, F234, -4567, world" | ||
| + | |||
| + | TestIntArray = ExplodeToIntArray$(TestString1,",",5) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then TestIntArray(0) =0 , TestIntArray(1)=12456 , TestIntArray(2)=0 , TestIntArray(3)=-4567 , TestIntArray(4)= 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: If a mixture of letters and numbers or just letters, then the result will always be 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|ExplodeToInt.fcfx|Explode To Int Array$ Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==ExplodeToFloatArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converts a string of numeric ASCII data that has been separated by a designator into a Float Array. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example if TestString = "Hello, 12.456, F23.4, -0.567, world" | ||
| + | |||
| + | TestFloatArray = ExplodeToFloatArray$(TestString , " , " , 5) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The delimiter must be enclosed within speech marks (double quotes). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then TestFloatArray(0) =0.000000 , TestFloatArray(1)=12.456000 , TestFloatArray(2)=0. 000000, TestFloatArray(3)=- , -0.567000 , TestFloatArray(4)= 0.000000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note: If a mixture of letters and numbers or just letters, then the result will always be 0. 000000. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|ExplodeToFloat.fcfx|Explode To Float Array$ Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==ImplodeFromIntArray$( Array<number>, delimiter<byte>, count<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converts Integer Arrays to a delimited string. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example if TestIntArray[0] = 2, TestIntArray[1] = 1234, TestIntArray[2] = -65, TestIntArray[3] = 0, TestIntArray[4] = 100 | ||
| + | |||
| + | TestString = ImplodeFromIntArray$(TestIntArray , ',' , 5) | ||
| + | |||
| + | As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ',' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then TestString = "2,1234,-65,0,100" | ||
| + | |||
| + | The string automatically adds the delimiters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|ImplodeFromIntArray.fcfx|Implode From Int Array Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
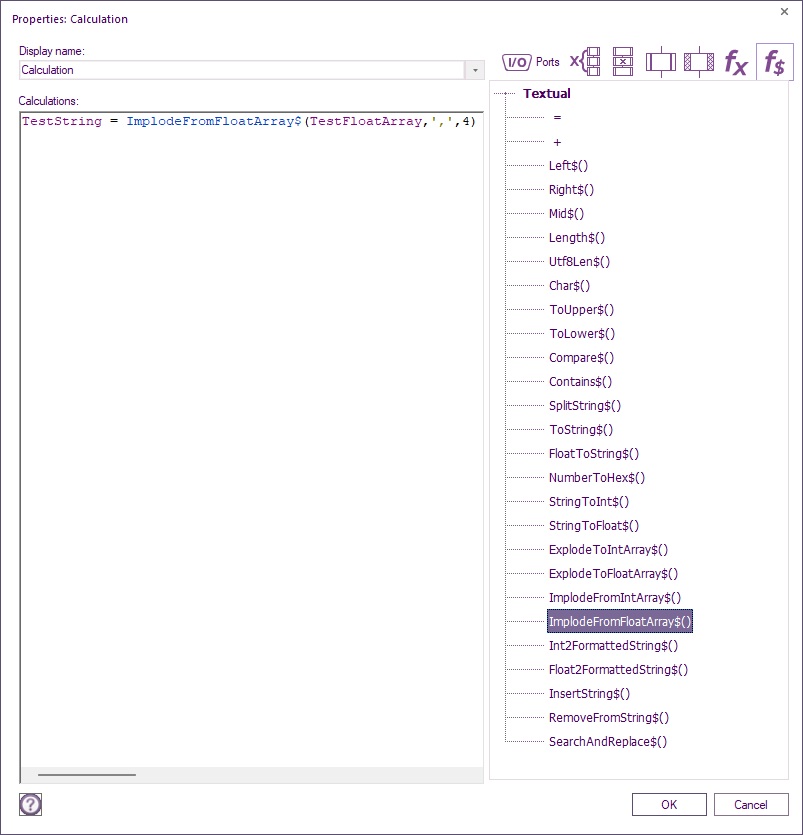
| + | ==ImplodeFromFloatArray$( Array<float>, delimiter<byte>, count<number>, precision<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converts Float Arrays to a delimited string with a specified amount of decimal places. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Example if TestFloatArray[0] = 2.123, TestFloatArray[1] = 1.234, TestFloatArray[2] = -65.2, TestFloatArray[3] = 0 | ||
| − | float = | + | Using TestString = ImplodeFromFloatArray$(TestFloatArray , ' , ', 4,2) |
| + | |||
| + | The delimiter must be enclosed within single quotes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then TestString = "2.12,1.23,-65.20,0.00" which is to 2 decimal places. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The string automatically adds the delimiters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ',' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|ImplodeFromFloatArray.fcfx|Implode From Float Array Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Int2FormattedString$( value<number>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Convert an integer to a formatted string with preceding padded characters | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the minimum total is greater then int length, then the difference will be total padded characters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example if integer is 1234 which is 4 characters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then if TestString = Int2FormattedString$(TestInt,6,'0'), then the result will be TestString = "001234" = Pad characters (00) + integer = 1234. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ',' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|Int2FormattedString.fcfx|Int To Formatted String Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Float2FormattedString( value<float>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte>, precision<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Convert a float to a formatted string with preceding padded characters | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the minimum total is greater then int length, then the difference will be total padded characters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example if float is 1234.612. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then if TestString = Float2FormattedString$(TestFloat,8,'0',1), then the result will be TestString = "001234.6" = Pad characters (00) + float + precision to 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | decimal place = 001234.6 | ||
| + | |||
| + | As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ',' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|Float2FormattedString.fcfx|Float To Formatted String Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==InsertString( main<string>, insert<string>, index<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Inserts a string within the main string starting at the index position. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example TestString1 = "Hello test1" & TestString2 = " World" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using TestString1 = InsertString$(TestString1,TestString2,5 ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The result would be "Hello World test1" | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|InsertString.fcfx|Insert String Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==RemoveFromString( text<string>, count<number>, index<number> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Removes a number of characters from a string starting at the index position | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example TestString = "Hello test1" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using TestString = RemoveFromString$(TestString,4,6) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The result will be TestString = "Hello 1" since the starting of the string "test" is at index position 6 since index starts at 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | test is 4 characters, hence test will be removed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|RemoveFromString.fcfx|Remove From String Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==SearchAndReplace(text<string>, search<string>, replace<string> )== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Replaces existing text with new text and returns number of changes made. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example TestString = "Hi,World Hi" | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using TestInt = SearchAndReplace$(TestString,"Hi,","Hello ") | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Hello " will replace Hi, hence the result will be "Hello World Hello" | ||
| + | |||
| + | The value of int returned is 2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Fcfile|SearchAndReplace.fcfx|Search And Replace Example}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Advanced String Functions Component= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Component:_Advanced_String_Functions_(Utility)|Click this link]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:08, 14 January 2025
Contents
- 1 String Functions
- 2 =
- 3 +
- 4 Left$(string, size)
- 5 Right$(string, size)
- 6 Mid$(string, start, size)
- 7 Length$(string)
- 8 Char$(string, number)
- 9 ToString$(value)
- 10 ToUpper$(string)
- 11 ToLower$(string)
- 12 Compare$(string1, string2, compare_type)
- 13 FloatToString$(float)
- 14 NumberToHex$(number)
- 15 StringToInt$(string)
- 16 StringToFloat$(string)
- 17 ExplodeToIntArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )
- 18 ExplodeToFloatArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )
- 19 ImplodeFromIntArray$( Array<number>, delimiter<byte>, count<number> )
- 20 ImplodeFromFloatArray$( Array<float>, delimiter<byte>, count<number>, precision<number> )
- 21 Int2FormattedString$( value<number>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte> )
- 22 Float2FormattedString( value<float>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte>, precision<number> )
- 23 InsertString( main<string>, insert<string>, index<number> )
- 24 RemoveFromString( text<string>, count<number>, index<number> )
- 25 SearchAndReplace(text<string>, search<string>, replace<string> )
- 26 Advanced String Functions Component
String Functions
The String functions are a set of string manipulation functions that can be used to edit, change and examine the strings.
To add a function, drag it into the calculation box or double click. The user can then edit this base code with the variables required.
| → | → | 
|
Example Strings used in explaining the functions below:
Str1[20]
Str2[20]
TestStr[40]
=
To assign a string value to a string variable you can simply use the = character.
Str1 = "Hello "
Str2 = "World"
Strings can also be treated like byte arrays to allow you to manipulate the individual bytes. For string data to work correctly with other string functions the end of the data must be signified with a 0 or null byte.
Str1[0] = 'H'
Str1[1] = 'e'
Str1[2] = 'l'
Str1[3] = 'l'
Str1[4] = 'o'
Str1[5] = ' '
Str1[6] = 0
Assigning a string constant to a string variable will automatically add the null byte to the end of the string for you.
Str1 = "Hello "
Strings can also be used with escape characters such as \n (newline), \r (carriage return), \t (tab), \xXX (hexadecimal byte value), \\ single backslash character.
Str1 = "Hello\n\rWorld"
+
Concatenates the two string together in the order presented from left to right.
If the resulting string is longer than the array size of the receiving string then any extra characters are lost.
Str1 = "Hello "
Str2 = "World"
TestStr = Str1 + Str2
TestStr is now "Hello World"
Multiple concatenations are best done like this to avoid using excess memory. Note that each line contains only two values to be added together.
TestStr = "Multiple " + Str1
TestStr = TestStr + Str2
TestStr is now "Multiple Hello World"
NOTE: Due to a limitation in generated code the result of multiple concatenations in one operation is limited to 20 characters. So the result of Str1 + Str2 + Str3 should not exceed 20 characters.
Left$(string, size)
Retrieves a substring from the string of size characters starting from the leftmost character.
If the length of the string used to store the result is less than size of the substring returned then any extra characters are lost.
TestStr = Left$(Str1, 3)
TestStr is now "Hel"
Right$(string, size)
Retrieves a substring from the string of size characters starting from the rightmost character.
i.e. a size of 4 retrieves the 4 rightmost characters.
If the length of the string used to store the result is less than size of the substring returned then any extra characters are lost.
TestStr = Right$(Str1, 3)
TestStr is now "lo "
Mid$(string, start, size)
Retrieves a substring from the string starting at position start of size characters. The first character of the string is at position zero.
If the length of the string used to store the result is less than size of the substring returned then any extra characters are lost.
TestStr = Mid$(Str1, 2, 3)
TestStr is now "llo"
Length$(string)
Retrieves the length of the string.
This is not the number of byte elements in the string variable, but the number of characters in the array before an ASCII Null character is encountered.
Str1 = "Hello "
RetVal = Length$(Str1)
RetVal is now 6
Char$(string, number)
Retrieves a single byte from the specified position in the string.
Str1= "Hello"
RetVal = Char$(Str1, 0)
Retval is now 'H'.
RetVal = Char$(Str1, 4)
Retval is now 'o'.
RetVal = Char$(Str1, 5)
Retval is now 0 (NULL terminator to mark the end of valid data).
String bytes can also be accessed directly using standard C square bracket array notation.
RetVal = Str1[4]
Retval is now 'o'.
ToString$(value)
Changes the numeric value or variable to a String.
TestStr = ToString$(1234)
TestStr is now "1234"
ToUpper$(string)
Changes all letters to upper case.
TestStr = ToUpper$(Str1)
TestStr is now "HELLO "
ToLower$(string)
Changes all letters to lower case.
TestStr = ToLower$(Str1)
TestStr is now "hello "
Compare$(string1, string2, compare_type)
Compares the two strings, parameters 1 and 2, and returns a BYTE value corresponding to the following results:
- 0 = strings are identical
- 1 = string1>string2
- 255 = string2>string1
The 3rd parameter, compare_type, determines whether or not the check is case sensitive. values for compare_type are:
- 0 = case sensitive
- 1 = case insensitive.
Examples
Str1 = "ABC"
Str2 = "abc"
RetVal = Compare$(Str1, Str2, 0)
RetVal is now 255 as Str2 is later in the ASCII sequence.
RetVal = Compare$(Str1, Str2, 1)
RetVal is now 0 as when case insensitive the two strings are identical.
Str2 = Str1
RetVal = Compare$(Str1, Str2, 0)
RetVal is now 0 as both strings are identical.
FloatToString$(float)
Converts a floating point number into a string.
float = Floating point number to convert.
string = String variable to hold the conversion data.
string = FloatToString(float, NumberOfDecimalplaces)
E.g to round a float to 2 decimal places you can use
string = FloatToString(float, 2)
The number of decimal places can be omitted so you can have
string = FloatToString(float)
NumberToHex$(number)
Converts a byte or int number into a hexadecimal string.
number = byte or integer number to convert.
string = String variable to hold the conversion data.
string = NumberToHex( number )
StringToInt$(string)
Converts a string of numeric ASCII data into an integer numeric data value.
string = String variable containing numeric ASCII data.
returns numeric data from the string in decimal form.
number = StringToInt$( string )
StringToFloat$(string)
Returns a string of numeric ASCII data into a floating point variable.
string = String variable containing numeric ASCII data.
returns numeric data from the string in floating point form.
float = StringToFloat$( string )
ExplodeToIntArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )
Converts a string of numeric ASCII data that has been separated by a designator into an integer Array.
Example if TestString = "Hello, 12456, F234, -4567, world"
TestIntArray = ExplodeToIntArray$(TestString1,",",5)
Then TestIntArray(0) =0 , TestIntArray(1)=12456 , TestIntArray(2)=0 , TestIntArray(3)=-4567 , TestIntArray(4)= 0
Note: If a mixture of letters and numbers or just letters, then the result will always be 0
ExplodeToFloatArray$( text<string>, delimiters<string>,max_count<number> )
Converts a string of numeric ASCII data that has been separated by a designator into a Float Array.
Example if TestString = "Hello, 12.456, F23.4, -0.567, world"
TestFloatArray = ExplodeToFloatArray$(TestString , " , " , 5)
The delimiter must be enclosed within speech marks (double quotes).
Then TestFloatArray(0) =0.000000 , TestFloatArray(1)=12.456000 , TestFloatArray(2)=0. 000000, TestFloatArray(3)=- , -0.567000 , TestFloatArray(4)= 0.000000
Note: If a mixture of letters and numbers or just letters, then the result will always be 0. 000000.
![]() Explode To Float Array$ Example
Explode To Float Array$ Example
ImplodeFromIntArray$( Array<number>, delimiter<byte>, count<number> )
Converts Integer Arrays to a delimited string.
Example if TestIntArray[0] = 2, TestIntArray[1] = 1234, TestIntArray[2] = -65, TestIntArray[3] = 0, TestIntArray[4] = 100
TestString = ImplodeFromIntArray$(TestIntArray , ',' , 5)
As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ','
Then TestString = "2,1234,-65,0,100"
The string automatically adds the delimiters.
![]() Implode From Int Array Example
Implode From Int Array Example
ImplodeFromFloatArray$( Array<float>, delimiter<byte>, count<number>, precision<number> )
Converts Float Arrays to a delimited string with a specified amount of decimal places.
Example if TestFloatArray[0] = 2.123, TestFloatArray[1] = 1.234, TestFloatArray[2] = -65.2, TestFloatArray[3] = 0
Using TestString = ImplodeFromFloatArray$(TestFloatArray , ' , ', 4,2)
The delimiter must be enclosed within single quotes.
Then TestString = "2.12,1.23,-65.20,0.00" which is to 2 decimal places.
The string automatically adds the delimiters.
As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ','
![]() Implode From Float Array Example
Implode From Float Array Example
Int2FormattedString$( value<number>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte> )
Convert an integer to a formatted string with preceding padded characters
If the minimum total is greater then int length, then the difference will be total padded characters.
For example if integer is 1234 which is 4 characters.
Then if TestString = Int2FormattedString$(TestInt,6,'0'), then the result will be TestString = "001234" = Pad characters (00) + integer = 1234.
As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ','
![]() Int To Formatted String Example
Int To Formatted String Example
Float2FormattedString( value<float>, min_length<number>, pad_char<byte>, precision<number> )
Convert a float to a formatted string with preceding padded characters
If the minimum total is greater then int length, then the difference will be total padded characters.
For example if float is 1234.612.
Then if TestString = Float2FormattedString$(TestFloat,8,'0',1), then the result will be TestString = "001234.6" = Pad characters (00) + float + precision to 1
decimal place = 001234.6
As the delimiter is a byte, if you want to enter as an ASCII character place within single quotes e.g. for a comma ','
![]() Float To Formatted String Example
Float To Formatted String Example
InsertString( main<string>, insert<string>, index<number> )
Inserts a string within the main string starting at the index position.
For example TestString1 = "Hello test1" & TestString2 = " World"
Using TestString1 = InsertString$(TestString1,TestString2,5 )
The result would be "Hello World test1"
RemoveFromString( text<string>, count<number>, index<number> )
Removes a number of characters from a string starting at the index position
For example TestString = "Hello test1"
Using TestString = RemoveFromString$(TestString,4,6)
The result will be TestString = "Hello 1" since the starting of the string "test" is at index position 6 since index starts at 0
test is 4 characters, hence test will be removed.
SearchAndReplace(text<string>, search<string>, replace<string> )
Replaces existing text with new text and returns number of changes made.
For example TestString = "Hi,World Hi"
Using TestInt = SearchAndReplace$(TestString,"Hi,","Hello ")
"Hello " will replace Hi, hence the result will be "Hello World Hello"
The value of int returned is 2